
IRES2.1
An integrated reliability and safety assessment software for modeling event tree and fault tree analysis in every industrial plant
DESCRIPTION
Reliability engineering is changing to a must in every industrial plants these days and the existence of such a thorough modeling software is needed more than before.
IRES is a complete package for analyzing every system which might be faulted in its lifetime. This analysis is implemented from event tree analysis, fault tree analysis, sensitivity and importance analysis and human reliability analysis point of view.
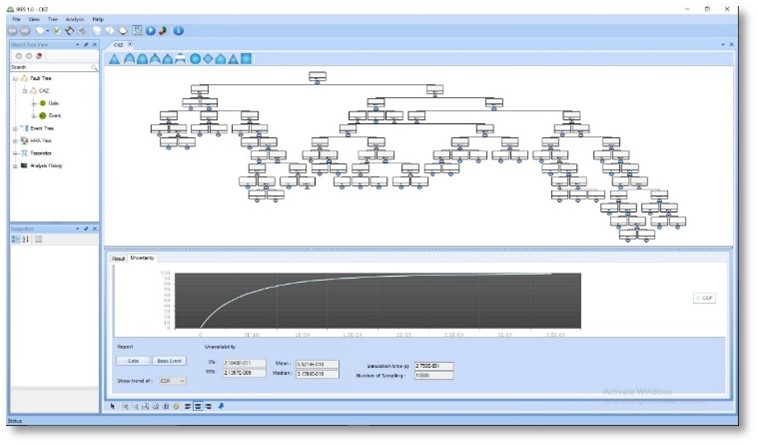
METHODOLOGY
IRES 2.1 benefits from the following well-proved algorithmic approaches:
- Four logical states for each event (true, false, normal and not);
- Two required quantification methods of Rare Event Approximation and Minimal Cut Upper Bound for calculating the basic events unavailability; furthermore, there are two optional quantification methods of 2nd-order and 3rd-order approximation for calculating the top event unavailability;
- There are six reliability models for basic event. It means that all of the industrial components could be categorized as Monitored, Repairable, Periodically tested, Constant unavailability, Fixed mission time, Constant frequency and Non-repairable components;
- Type of calculation is divided into two modes: Simple quantification which ignores negated basic events in minimal cut set, and DeMorgan rules which calculates unavailability of negated basic events in minimal cut sets in fault tree.
- Unavailability calculation of every basic event is carried out by point-estimate or uncertainty analysis for parameters. In uncertainty analysis there are six probability distribution function: Beta and Gamma functions, Gaussian (normal), Log-normal, Uniform, and Log-uniform distributions. It is necessary to mention that the simulation of all of the parameters in basic event reliability models are included in these six distribution functions.
- All of the main three models of Common Cause Failures (CCFs) are implemented in IRES 2.1; Beta factor model, Multiple Greek Letter (MGL) model and Alpha factor model.
- One of strong points of IRES 2.1 is the modeling of all types of gates. It means that user can model their scenario based on the gates AND, OR, N-out of M, XOR, NAND, and NOR. All of these gates could be transformed to fundamental AND/OR gates finally.
- Three types of cut-offs truncation have been considered for reduction the amount of computational work involved in minimal cut set generation: Absolute cut-off value, relative cut-off value, and cut-off by order.
- Minimal cut set generation is applied based on the sophisticated algorithm which is used in RiskSpectrum software.
- Fussell-Vesley importance model and sensitivity calculations are carried out after the calculation of the top event.
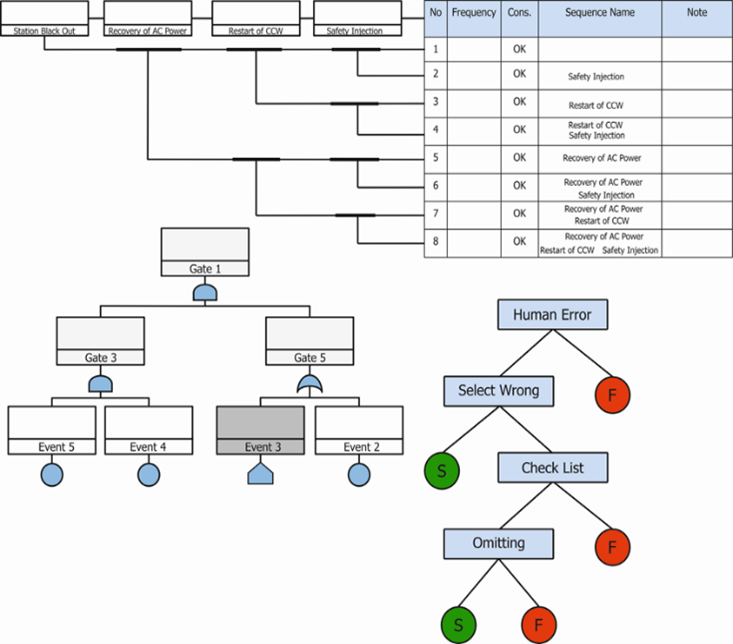
- IRES 2.1 benefits from human reliability analysis model and human error binary tree. HRA has long been recognized that human error has a substantial impact on the reliability of complex systems. Technique for human error rate prediction (THERP) model, the oldest and most widely used HRA technique, uses conventional system reliability analysis modified to account for possible human error. Instead of generating equipment system states, THERP produces possible human task activities and the corresponding error probabilities.
FEATURES
Followings are the major capabilities of IRES 2.1:
- Probabilistic safety assessment using fault tree and event tree analysis.
- Ability to use different gates such as AND, OR, NAND, NOR, N/M and XOR in a fault tree.
- Ability to define various events like basic event, house event and undeveloped event in fault trees.
- Supporting Common Cause Failure (CCF) model calculation.
- Use of transfer gate in large fault trees.
- Ability of Human Reliability Analysis (HRA).
- Supporting uncertainty, sensitivity and importance analysis.
- Developing event trees include making various sequences, link to fault trees and consequences analysis.
- User-friendly interface and graphical output display.
APPLICATIONS
IRES 2.1 is especially developed to be an integrated software for industrial probabilistic safety assessment which have following purposes:
- Quantitative and qualitative safety assessments,
- Providing a commercial software contains essential features modeling real-world problems in PSA.
The software covers a wide range of needs for students, researchers and engineers in probabilistic safety/risk assessment. IRES 2.1 is applicable for probabilistic safety assessment of any industrial facilities or engineering systems which is exposed to hazards to evaluate probabilities of system components failures and frequency of undesirable consequences.
It should be noted that IRES 2.1 is not applicable in data mining of component failures and system faults. Subsequently, this software uses those data as inputs to model a specific failure/success situation in a system.
Every system failure/success is modeled by a fault tree and every component of the system is modeled as a basic event with a specific reliability model and its related data. The outcome of a fault tree is probability of its top event, for example, probability of fire protection system failure (top event) which contains some features or subsystems.
The whole scenario of an accident, which contains initial event, function events, accident sequences and consequences, is modeled by an event tree. One output of an event tree is frequency of undesirable consequences final state.
The last but not the least, would be display tools planned for the software to bring a rather suitable show of parameters for the user. This surely makes the software admissible for the engineers as they frequently need to compare and contrast evaluated data with minimum effort but maximum efficiency.

