KAVOSH1.0
An advanced computational software for 3D thermo-neutronic analysis of PWR cores & multi-parameter loading pattern optimization
INTRODUCTION
KAVOSH, meaning exploration, is an advanced computational software planned for 3D thermo-neutronic analysis of PWR cores plus multi-parameter optimization of core loading pattern. It is indeed a combination of two main programs, ALVAND 1.0 and OPTICORE 1.0, both finalized by the I. R. Iran’s Advanced Nuclear Computing Center (ANCC), for core analysis and loading pattern optimization, respectively. The software consists of a variety of solvers for treating hexagonal and rectangular shaped reactors. Forward (direct) and backward (adjoint) diffusion equations are solved via a number of nodal and finite element subroutines empowered with accelerating approaches as well as parallel processing techniques to speed-up the calculations and to reduce the computational cost.
The entire system has been verified using various benchmarks and reference data found in published reports, as well as, comparisons made mainly against PARCS outputs. Excellent agreements found in almost all cases which bring a meaningful trust for the users. Yet, V&V is still going on for more certitude.
KAVOSH 1.0 is currently (Sep. 2022) under finalization and a graphical user interface is supposed to be developed for, making its application as simple as possible. It is supposed to be released in late 2023 by ANCC. Future developments mainly contains enabling dynamic features as well as plug-ins to a number of external TH codes (like RELAP) to realize accident analysis and improved time-dependent core TH evaluations.
METHODOLOGY
KAVOSH 1.0 benefits from the following well-proved numerical approaches to deal with the two-group forward and adjoint diffusion equations:
-
Nodal Expansion Method;
-
Coarse Mesh Finite Difference Method; and,
-
Finite Element Method.
In addition, the heat conduction equation is solved via the simple but efficient single phase multi-channel approach which preserves needed speed along with sufficient accuracy for a wide range of real core thermal-hydraulic performances.
Also, optimizing the core loading pattern is currently provided by the Simulated Annealing Algorithm with objective functions encapsulating several sorts of parameters of interest e.g. neutronic, thermal-hydraulic, economic and safety ones limited by certain user-defined constraints. More optimization algorithms are under investigations at this time for future releases.
FEATURES
Followings are the major capabilities of KAVOSH 1.0:
-
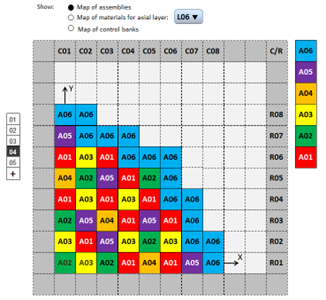
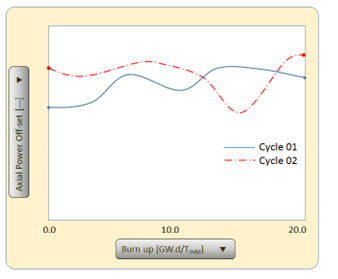
BOC to EOC estimation of effective multiplication factor, critical Boron concentration, burn up, peaking factors, poison (135Xe & 149Sm) densities, reactivity coefficients, axial power off-set, prompt and delayed neutron life-time, fuel and moderator temperatures, control rod worth, etc.
-
Ability to plan start-up procedure and power maneuvers throughout cycles by regulating control rods.
-
Multi-cycle (up to 99) core analysis and reload options.
-
Empowered with accelerating approaches as well as parallel processing techniques to speed-up the process and to minimize the computational cost.
-
Multi-parameter core optimization regarding pattern constraints and limitations.
-
Multi-cycle pattern optimization and equilibrium cycle search option.
-
Supporting PMAXS data library, and,
-
User-friendly interface and graphical output display.
APPLICATIONS
KAVOSH 1.0 is especially developed for two main purposes:
-
PWR core design and analysis, and,
-
PWR core loading pattern optimization.