
TORANJ 2.0
A Software to Create Neutronic and Kinetic Data in PMAXS Format
DESCRIPTION
In order to perform realistic core calculations in a deterministic approach, material group constants and kinetic parameters representative of the actual local conditions by considering burn-up effects of a nuclear reactor core should be produced. For this purpose, the TORANJ software is developed by the I. R. Iran’s Advanced Nuclear Computing Center (ANCC). TORANJ produces data in “tree-leave” structure and stores them in the PMAXS format. The PMAXS file is constructed using the output of the lattice code and regards to the specific format that can be read by PARCS (Three-dimensional reactor core simulator). TORANJ can employ WIMSD or DRAGON as the lattice code based on the user’s choice. Moreover, TORANJ has been equipped with a flexible Graphical User interface (GUI) for input and output handling.
In order to verify TORANJ, different PMAXS files for a wide variety of Light and Heavy Water Reactors (LWRs & HWRs) are generated. Thereafter, core operating parameters such as multiplication factor, radial and axial power distribution, fuel cycle length, etc. from PARCS are compared with reference data found in published reports.
Considering the current status of TORANJ, further enhancements have been considered for the future. Some of these improvements include capability of generating form function both in rectangular and in hexagonal lattices (although for the latter an extension to PMAXS format is needed) and generating adjoint weighted kinetic parameters based on what the DRAGON code offers.
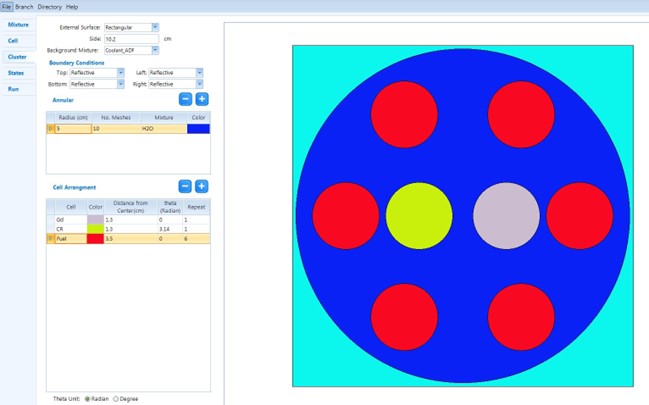
METHODOLOGY
TORANJ gets the user-specified lattice code (WIMSD5b, DRAGON4, or DRAGON5), microscopic library, geometry specifications, material composition, and solver setting parameters (e.g. self-shielding model, type of eigenvalue search problem, etc.). Also, to construct a PMAXS tree-leave structure, TORANJ receives burn-up, branches and history information from the user. Then, TORANJ makes an appropriate input for the WIMS or DRAGON lattice code for each set of state variables (response to each history or branch) and after running it, uses the output of the specified lattice code to create the PMAXS file. The PMAXS files contain all the cross-section data, the fission yields for I-135, Xe-135, AND Pm-149, the microscopic absorption cross-sections of Xe-135 and Sm-149, etc.
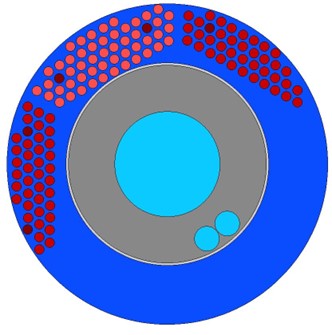
FEATURES
Followings are the main features of TORANJ:
- Ability to model complex geometries and using different classes of transport solvers (collision probability, method of characteristics, etc.) and self-shielding models (Equivalence, subgroup, and Tone) based on the Dragon 5 code.
- Capability to simulate a wide variety of reactor types such as: light and heavy water reactors and new generation ones (SMR, etc.);
- Possibility of separating coolant and moderator (suitable for heavy water reactors);
- Run in parallel (motley CPU) with the ability to generate and use a backup file;
- Taking advantage of the flexible and easy to handle GUI.
- Ability to export input of the WIMS or DRAGON code, for any user-specified simulation, from the TORANJ’s output handler.
APPLICATIONS
TORANJ can serve as a dynamic library generator for core calculation codes. It has capability to simulate 2D cells of PWR, WWER, CANDU, and any other innovative reactor type. This dynamic library generator is equipped with both DRAGON and WIMS lattice codes which allows code-to-code comparisons to be provided.

